
Thus, the atomic number equals the total number of electrons. This is because in an uncharged or in zero charge state the total positive charge produced by the proton is nullified by the negatively charged electrons revolving around the nucleus. Note: Sometimes we refer to the atomic number as the number of electrons present in an atom of an element. Adapted from Understanding Radiation (EPA). The atomic number of carbon is 6, which tells you the number of protons and. Therefore the atomic mass of carbon is 12. Carbon-14: with 6 protons and 8 neutrons, and an atomic mass of 14. A carbon atom contains 6 protons, 6 electrons, and either 6 (carbon-12), 7 (carbon-13), or 8 (carbon-14) neutrons. The carbon has 6 protons and 6 neutrons present in the nucleus which stabilizes the nucleus. The Z is equal to the charge number of the nucleus. The atomic number is a unique identity of a chemical element. The elements silicon, germanium, tin and lead are also in group 14. The atomic number of the element is represented by the symbol Z. Carbon in the Periodic Table Carbon, with atomic number 6 and symbol C, likes in group 14 of the periodic table, to the right of boron and the left of nitrogen.
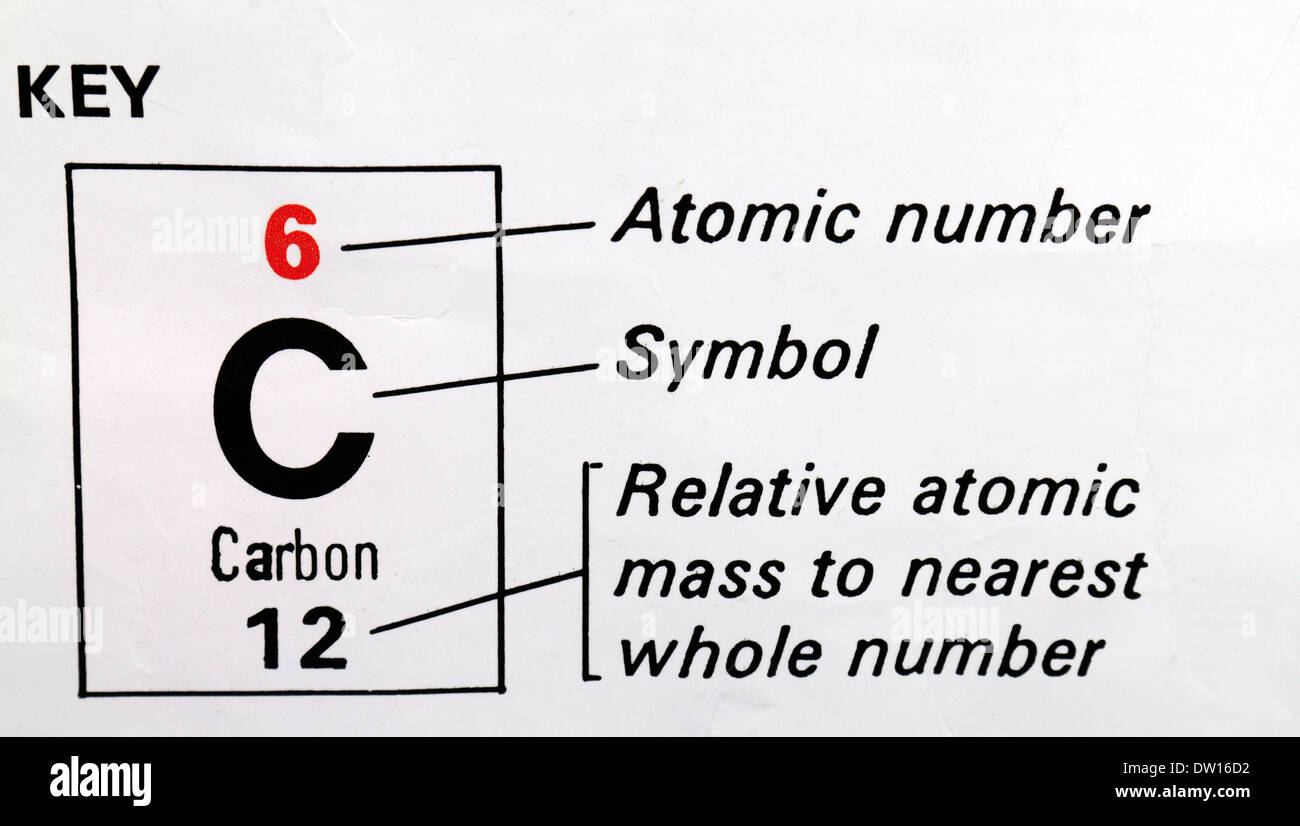
The atomic number of an element equals the protons found in the nucleus of an atom. The carbon atom has 6 protons in its nucleus and 6 electrons revolving around the nucleus in an uncharged state. Melting Point: 3500.0 C (3773.15 K, 6332.0 F) Boiling Point: 4827.0 C (5100.15 K. The atomic mass of an atom is the number of protons and neutrons. All carbon atoms have 6 protons in their nucleus. Carbon has some similarities to the metalloid silicon, but silicon cannot be the basis for life like carbon can. In the periodic table, the atomic number increases as we move from left to right and top to bottom. For example carbon has an atomic number of 6. Carbon, with atomic number 6 and symbol C, likes in group 14 of the periodic table, to the right of boron and the left of nitrogen.

It has 6 protons (which defines it as carbon) and has 7 neutrons. Hint: The atomic number is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus. Carbon 13 refers to a specific type of carbon that has an unusual number of neutrons, causing it to have an atomic mass of 13.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
